Author: Angus McLachlan | Posted On: 31 Mar 2025

As AI adoption accelerates, the energy demands of large-scale data centre infrastructure are soaring. This AI Power Race is driving tech giants to future-proof their energy supply to support ever-expanding AI workloads. With data centres already among the world’s largest electricity consumers—and AI models vastly more energy-intensive than conventional cloud computing—access to scalable clean energy has become a strategic imperative. The International Energy Agency estimates global electricity demand from data centres could double 2022 levels by 2026—a surge roughly equivalent to adding the combined electricity consumption of the UK and Australia.
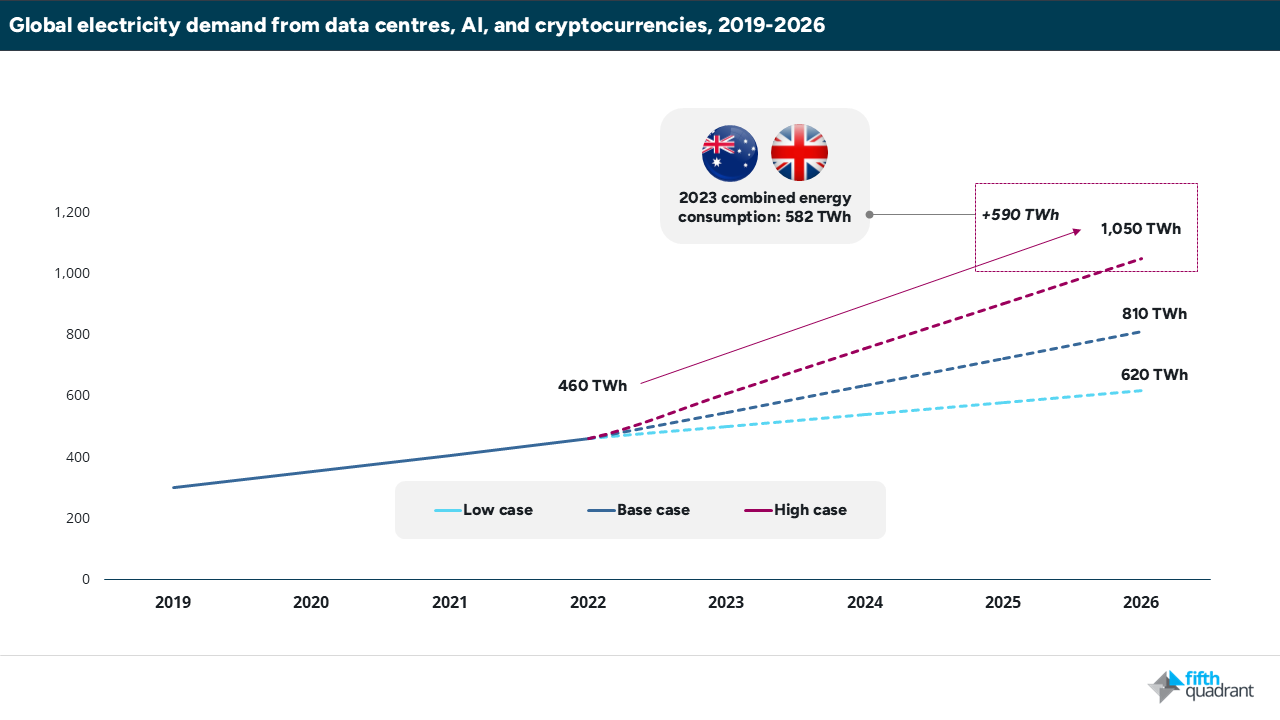
Beyond surging energy demands, three additional factors are driving tech giants to rethink their energy strategies:
- Grid reliability: AI systems demand constant uptime, making resilience a priority. Companies are investing in microgrids, battery storage, and backup systems to ensure performance even during grid disruptions.
- ESG requirements: Heightened scrutiny from investors, regulators, and the public is pushing firms to align AI expansion with emissions reduction and broader climate commitments.
- Cost control: As electricity becomes one of the largest operational costs for AI infrastructure, tech companies are securing long-term energy contracts and investing in efficiency to manage expenses and protect margins.
This article examines how Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are reimagining their energy strategies to meet the twin challenges of AI growth and climate responsibility.
Google – 24/7 Carbon-Free Energy
Google is taking a pioneering approach to energy strategy by committing to power all its data centres with 24/7 carbon-free energy by 2030. This strategy goes beyond traditional offsetting and aims to match clean electricity to real-time usage at every location.
Key measures:
- Long-term PPAs for wind and solar across continents.
- Investing in enhanced geothermal technology through a partnership with Fervo Energy.
- Exploring next-generation nuclear solutions, including a partnership with Oklo to deploy Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) as a potential source of consistent, zero-carbon baseload power.
Google’s approach positions the company as not only a major clean energy consumer, but also a key force in accelerating innovation and investment across the clean energy ecosystem.
Microsoft – SMR Innovation
Microsoft, like Google, is actively exploring Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology to deliver consistent, carbon-free baseload power—critical to supporting the future energy demands of AI and cloud infrastructure.
Key measures:
- Committed to becoming carbon negative by 2030.
- Exploring Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and recruiting nuclear experts to evaluate their feasibility.
- Signed a 20-year nuclear energy agreement with Constellation to power data centres with zero-emissions baseload power.
Microsoft’s rapid AI-driven infrastructure growth may temporarily push it above carbon neutrality, but this appears to be a calculated step toward its longer-term goal of becoming carbon negative by 2030— by prioritising clean energy investments today to support more substantial emissions reductions in the future.
Amazon – Distributed Energy Networks
Amazon, through AWS, is focussing on distributed energy solutions to support the growing energy demands of its data centres while contributing to a more decentralised and resilient energy grid.
Key measures:
- Pledged to use 100% renewable energy by 2025 and currently the largest corporate purchaser of renewables globally.
- Investing in localised microgrid infrastructure to enhance regional grid resilience.
- Deploying on-site battery storage to manage peak loads and reduce reliance on centralised power supply.
Amazon’s shift toward distributed generation, localised storage, and grid-interactive technologies highlights its growing role in building smarter, more resilient energy networks that can support both its operations and surrounding communities.
The Quiet Battleground Behind AI’s Rise
As the scale and complexity of AI workloads accelerate, energy is no longer just an operational input—it’s a defining constraint and a key differentiator. Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are each approaching this challenge with distinct strategies, but all recognise that the future of AI is inseparable from the future of clean energy. Whether through 24/7 carbon-free matching, SMR innovation, or distributed energy resources, these major players are not only securing energy for their own operations—they’re also shaping the future of how AI and clean power will coexist. As demand continues to surge, aligning compute growth with low-carbon, high-reliability energy systems will be essential to both environmental responsibility and long-term competitiveness.
Fifth Quadrant is a leader in energy transition market research and AI research. For any questions or inquiries, feel free to contact us here.
Posted in Uncategorized

