Author: Jessica McMahon | Posted On: 27 Mar 2025
Australia’s business scene is evolving, driven by a post-pandemic shift that saw city dwellers trade urban hustle for regional tranquility. The COVID-19 pandemic fuelled the “tree-change” movement, reshaping where and how businesses thrive. In short, the tree change movement is a term used to describe those people leaving the city and moving to regional or rural areas for a quieter, greener, and more nature-focused lifestyle. It’s driven by things like wanting a better work-life balance, escaping the hustle and bustle, and making the most of more affordable living. Affordable properties, robust community support, and the growing feasibility of remote work have combined to inject fresh talent and diversity into regional economies.
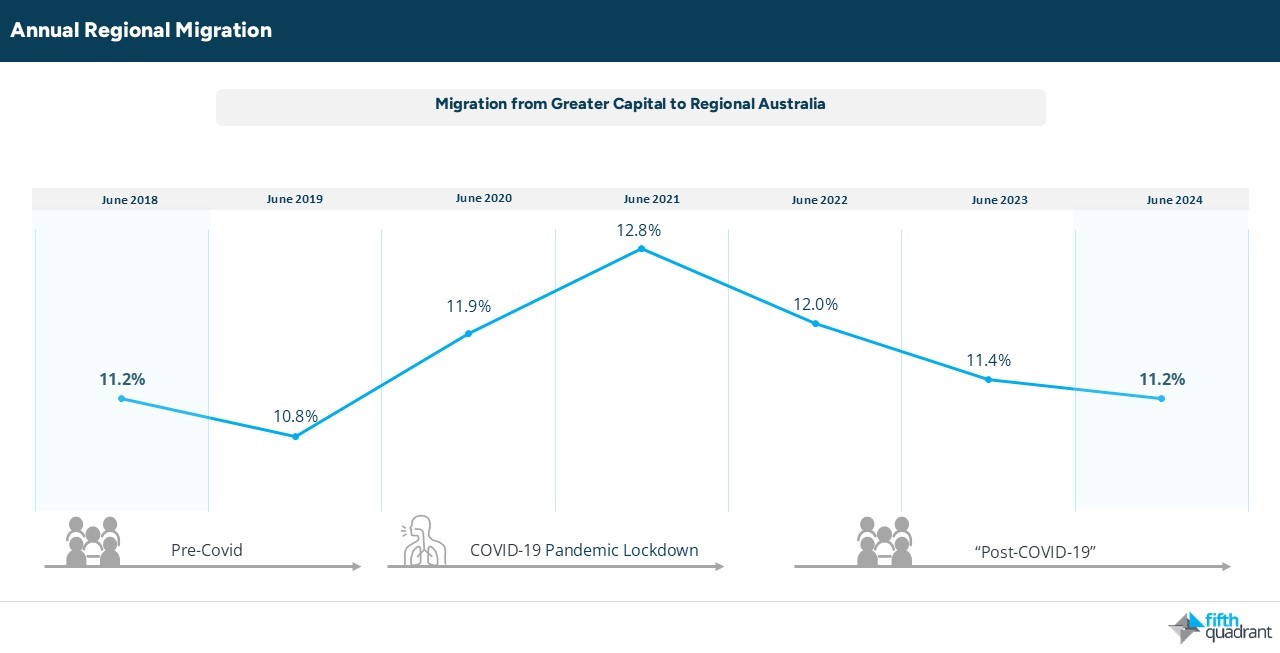
A Surge in Regional Migration
Between 2020 and 2021, regional areas experienced faster population growth than capital cities for the first time since 1993–94. This trend was influenced by lower net overseas migration and a decline in movement from regional areas back to cities. The appeal of regional living continues to be strong, with data from the Commonwealth Bank revealing that 11.2% of all relocations are now from cities to regional areas, a trend that has remained strong since the pandemic.
Millennials are the most frequent demographic to move to regional Australia. Most would assume this is largely due to inflated metro house prices. But it’s not all about affordability – people are chasing a different way of life; whether it’s remote working, starting their own business, or shifting into community-focused roles.
Seizing Opportunities in Regional Areas
This population shift has helped fuel a surge in regional business growth, with 31% of small businesses in Australia thriving outside major cities. Westpac data reveals that business lending in regional areas surged by 12.4% over this period —outpacing the 11.3% growth observed in metropolitan regions. Regional areas are also less saturated than their metro counterparts, offering businesses greater opportunities to establish themselves and face less direct competition. Similarly, with fewer corporate job opportunities, many internal and external migrants are turning to business ownership in the hospitality space, which has led to an expansion in café culture and over half of craft breweries being situated in regional Australia. Supporting this, data from our SME Sentiment Tracker shows that business ownership is 8% more prevalent in regional Australia than in metro areas.
Looking Ahead
This shift toward regional living is not only changing population patterns but it is also influencing Australia’s small business landscape. Regional areas are benefiting from growth investment and innovation, as they continue to draw in more skilled workers. This growth, which can be reflected in a rise in patents and entrepreneurial activity, is positioning regional hubs as dynamic centres for business and community-driven enterprise.
Beyond a lifestyle change, the tree-change trend is contributing to the development of resilient, locally driven economies. With governments and financial institutions recognising this shift, support for regional entrepreneurs is expanding. As investment continues to rise, regional business communities appear well-positioned for long-term growth and innovation.
Keep up to date with the latest B2B market research and SME Insights from Fifth Quadrant here. For any questions or inquiries, feel free to contact us here.
Posted in Uncategorized, Financial Services, QN, Social & Government

